
Data Structures Write Up
Blog Python Model code and SQLite Database.
- From VSCode using SQLite3 Editor, show your unique collection/table in database, display rows and columns in the table of the SQLite database.
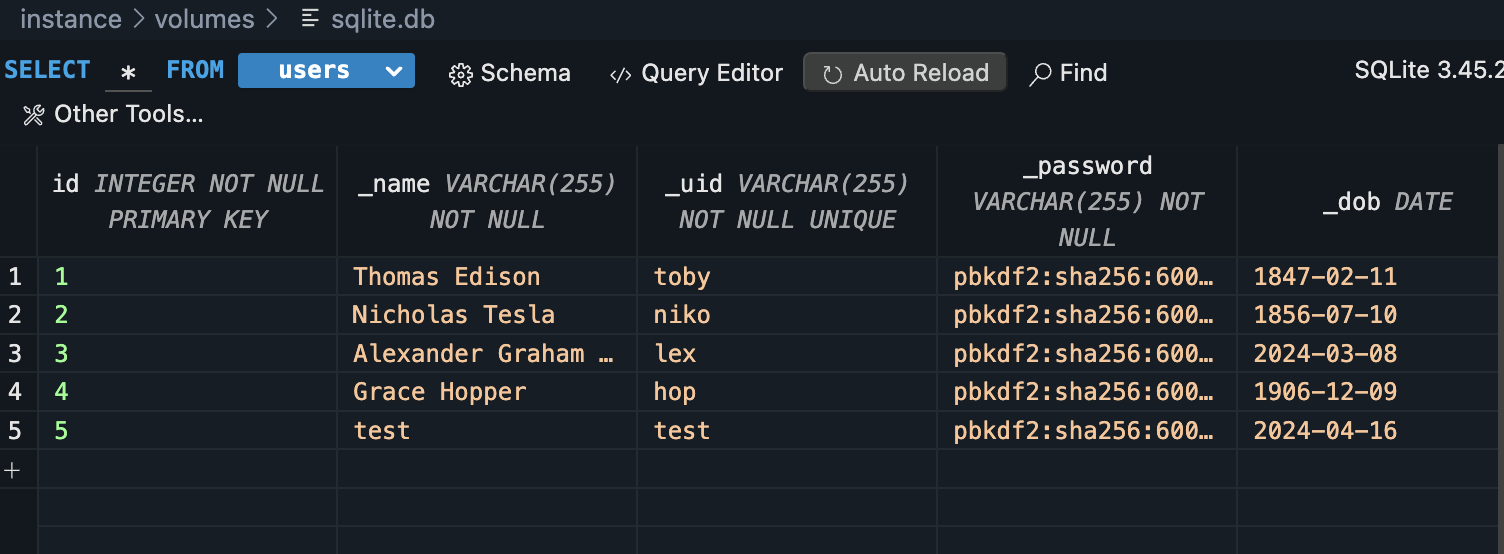
- There are multiple rows for each entry, and each column is a different data point (name, uid, join date, etc.). First 4 entries are preset by DB, and the others are added users. This DB can be used to add a lot of users, and can be scaled easily to allow for more users.
- From VSCode model, show your unique code that was created to initialize table and create test data.
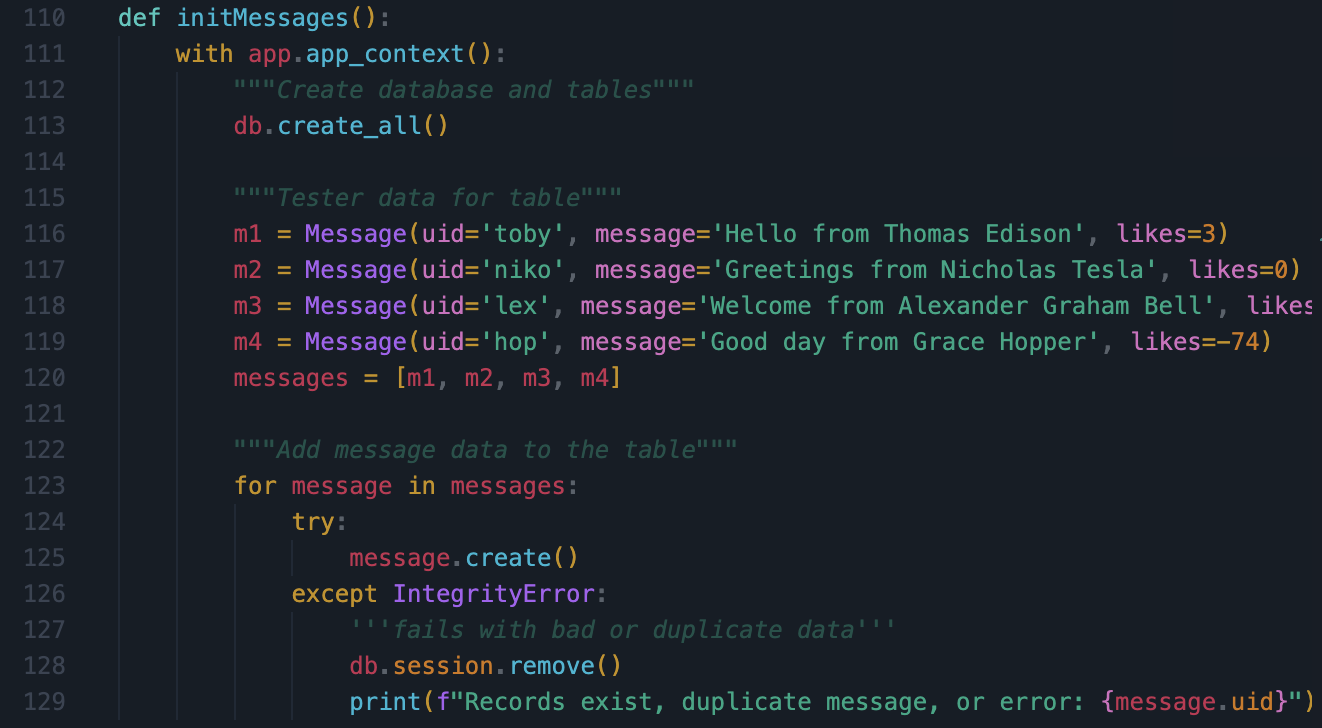
- Adds test information to the database to make sure the main file has run properly. The users added can be seen in the first 4 rows of the DB
Lists and Dictionaries
- In VSCode using Debugger, show a list as extracted from database as Python objects.
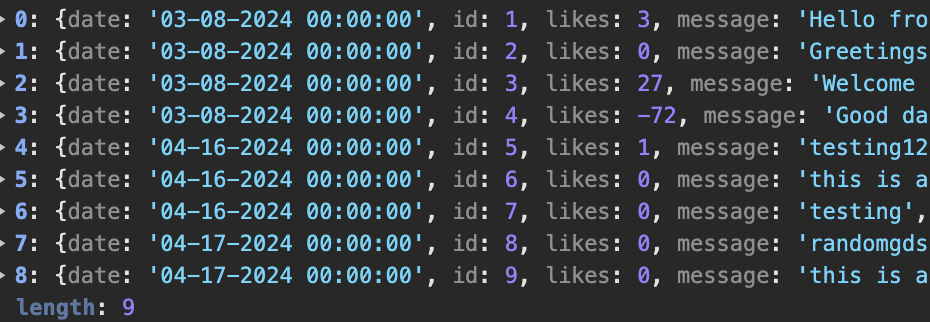
- Shows all the messages using the GET function as a dictionary (date added, likes, message body, etc.) Function accessed by frontend to display messages to users.
- In VSCode use Debugger and list, show two distinct example examples of dictionaries, show Keys/Values using debugger.
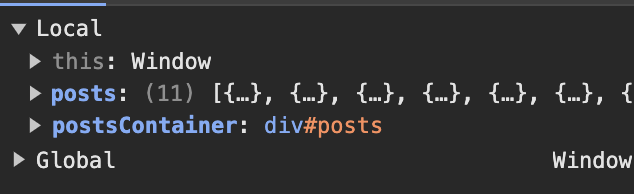
- Shows the information from the GET function as dictionaries in a big list. This data can be iterated for the frontend to deal with the data.
Blog Python API code and use of Postman to request and respond with JSON.
- In VSCode, show Python API code definition for request and response using GET, POST, UPDATE methods. Discuss algorithmic condition used to direct request to appropriate Python method based on request method.
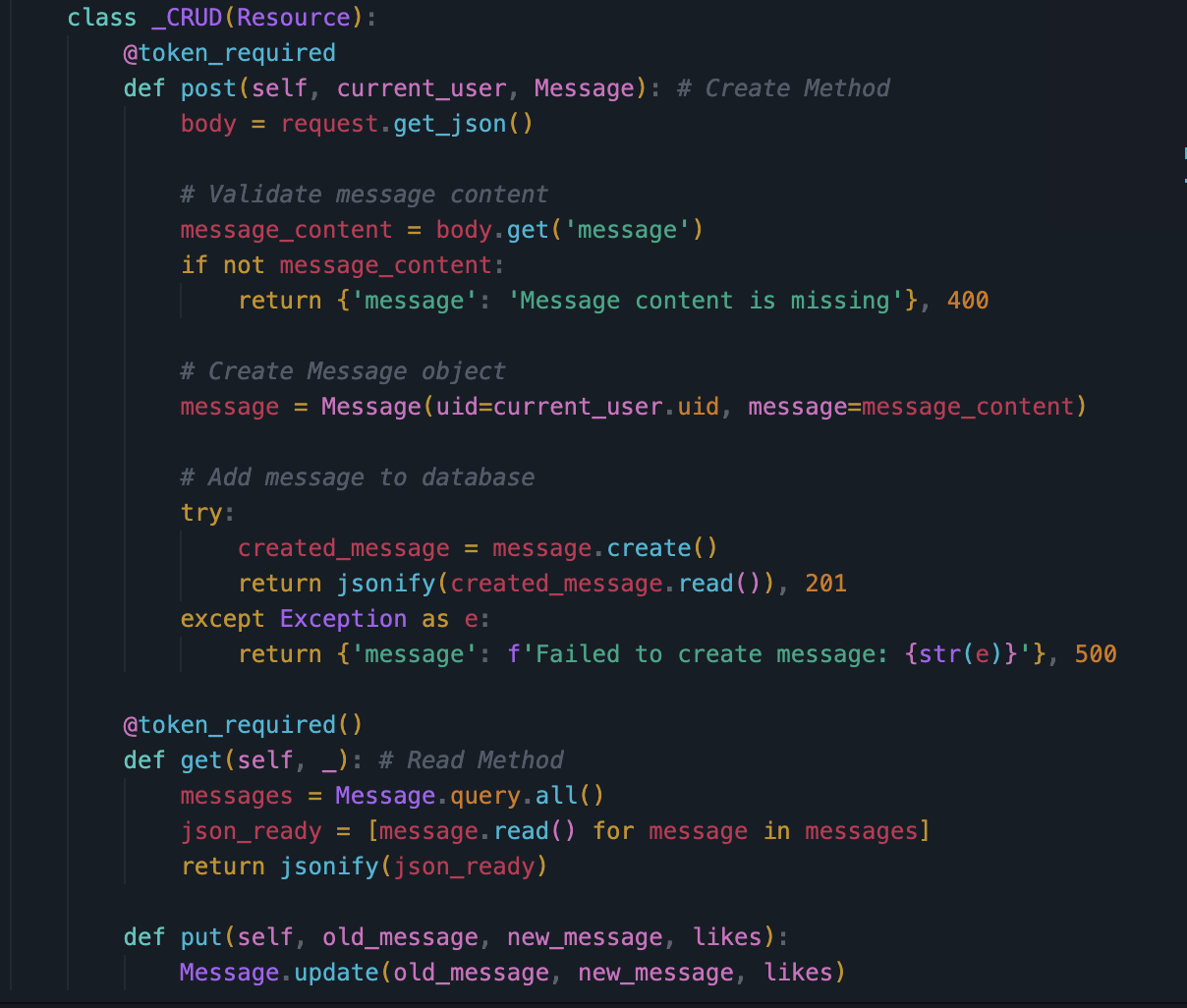
- Shows POST, GET, and PUT functions in the python API file. POST function adds info, GET function returns info from DB, PUT function updates existing data. Frontend uses these functions by using the fetch() function
- In VSCode, show algorithmic conditions used to validate data on a POST condition.

- Uses an algorithmic condition (if message content not missing) to check if data was sent, else return 400 error. Makes sure that an error is not displayed so that all the messages are blank.
- In Postman, show URL request and Body requirements for GET, POST, and UPDATE methods.

- Message, likes, and cookies required for POST request to make sure the user is authenticated/sent all the data needed for a message

- Cookies required for GET request to make sure only users can see the messages.

- Message required for update method so the original message can be found
- In Postman, show the JSON response data for 200 success conditions on GET, POST, and UPDATE methods.
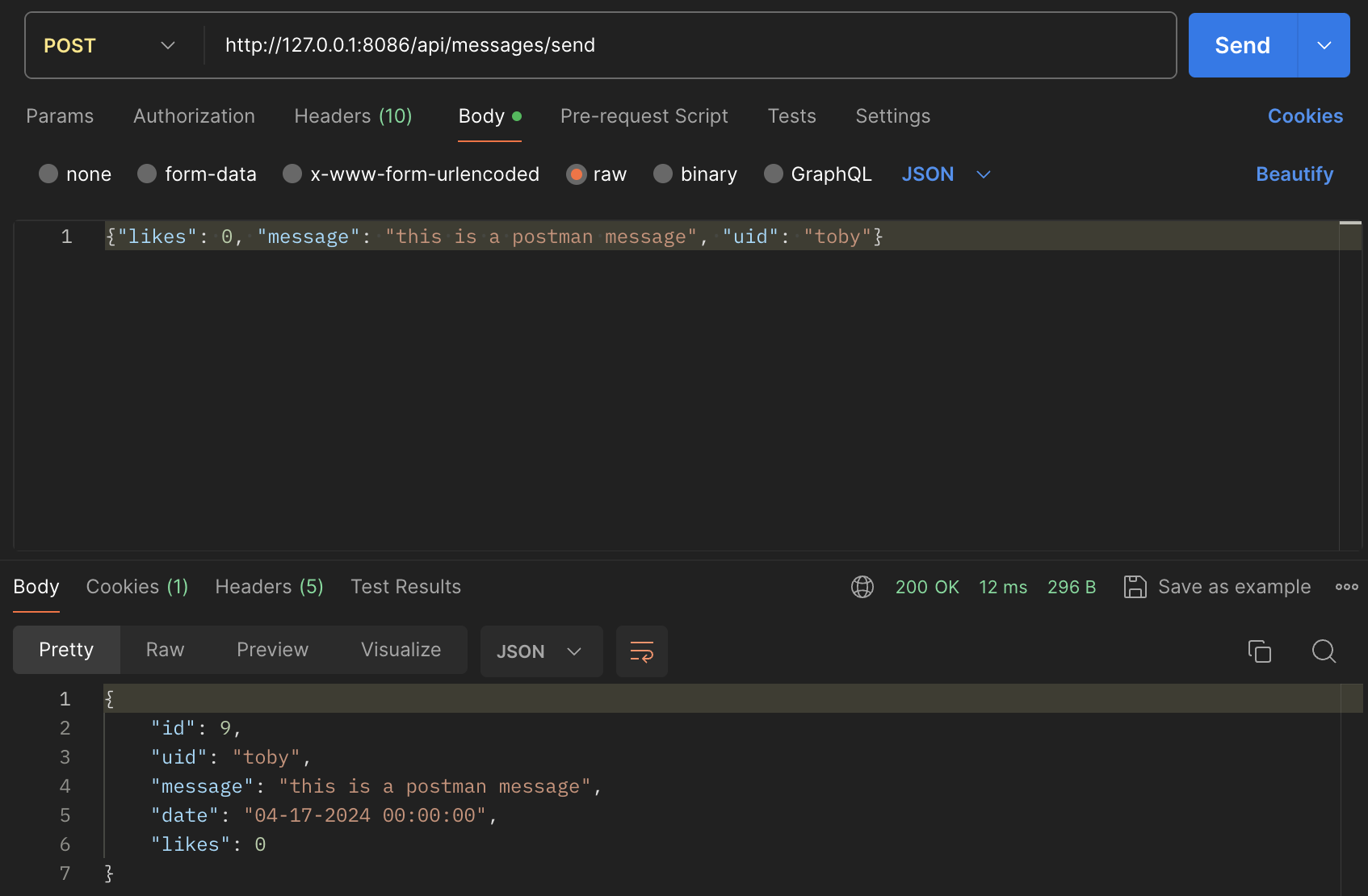
- New message from POST function is returned to display on frontend as a new message
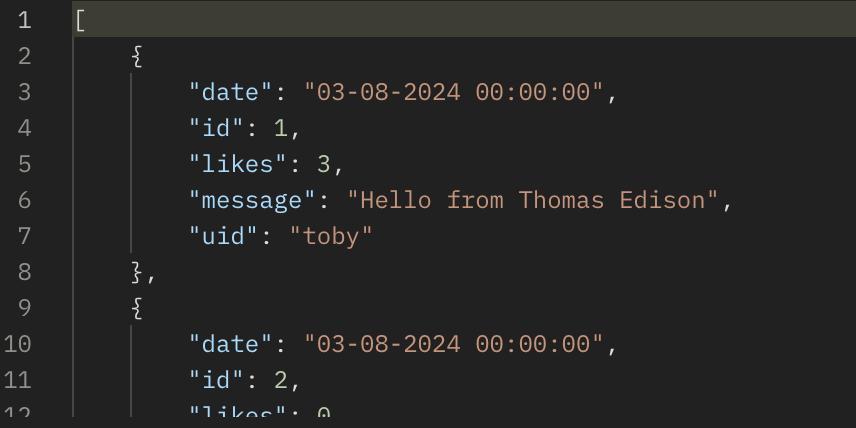
- All messages are returned to display in the messages page on frontend

- The new value of the changed object is returned to update the display
- In Postman, show the JSON response for error for 400 when missing body on a POST request.

- There is a format error sent because there is no info given for the required field
- In Postman, show the JSON response for error for 404 when providing an unknown user ID to a UPDATE request.
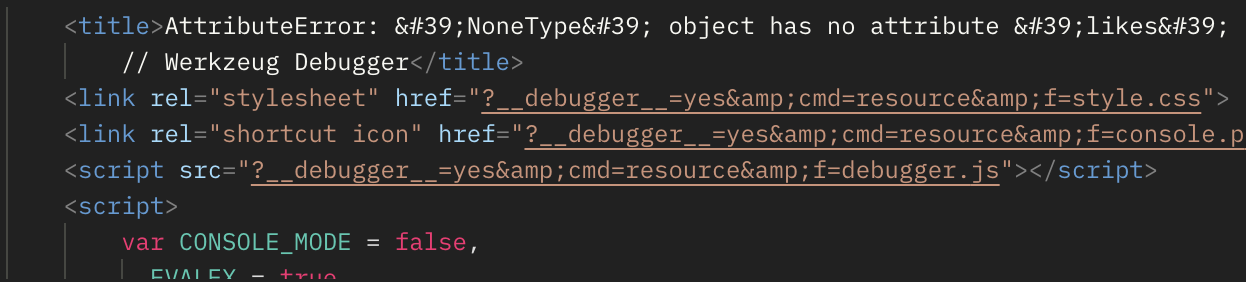
- NoneType error because the message doesn’t exist
Blog JavaScript API fetch code and formatting code to display JSON.
- In Chrome inspect, show response of JSON objects from fetch of GET, POST, and UPDATE methods.
- GET response
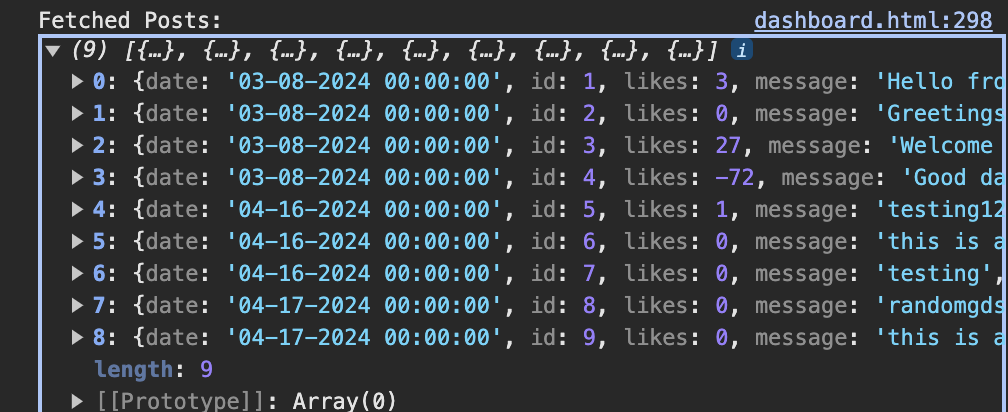
- All the previous posts from the database are shown as a collection of dictionaries from the GET request. This data can be shown by accessing elements of the dictionary to show on frontend.
- POST response

- The message that was posted using POST function is returned so the frontend can display the newly shown message
- UPDATE response

- The new value for the updated value is shown so the frontend can update the display counter.
- In the Chrome browser, show a demo (GET) of obtaining an Array of JSON objects that are formatted into the browsers screen.

- Shows the different entries from the database as seperate messages as seen above
- In JavaScript code, describe fetch and method that obtained the Array of JSON objects.
- By getting the hostname of the browser and adding ‘/api/messages/send’, the data inputted in frontend is sent to backend, and the message in the database is returned back to frontend
- In JavaScript code, show code that performs iteration and formatting of data into HTML.
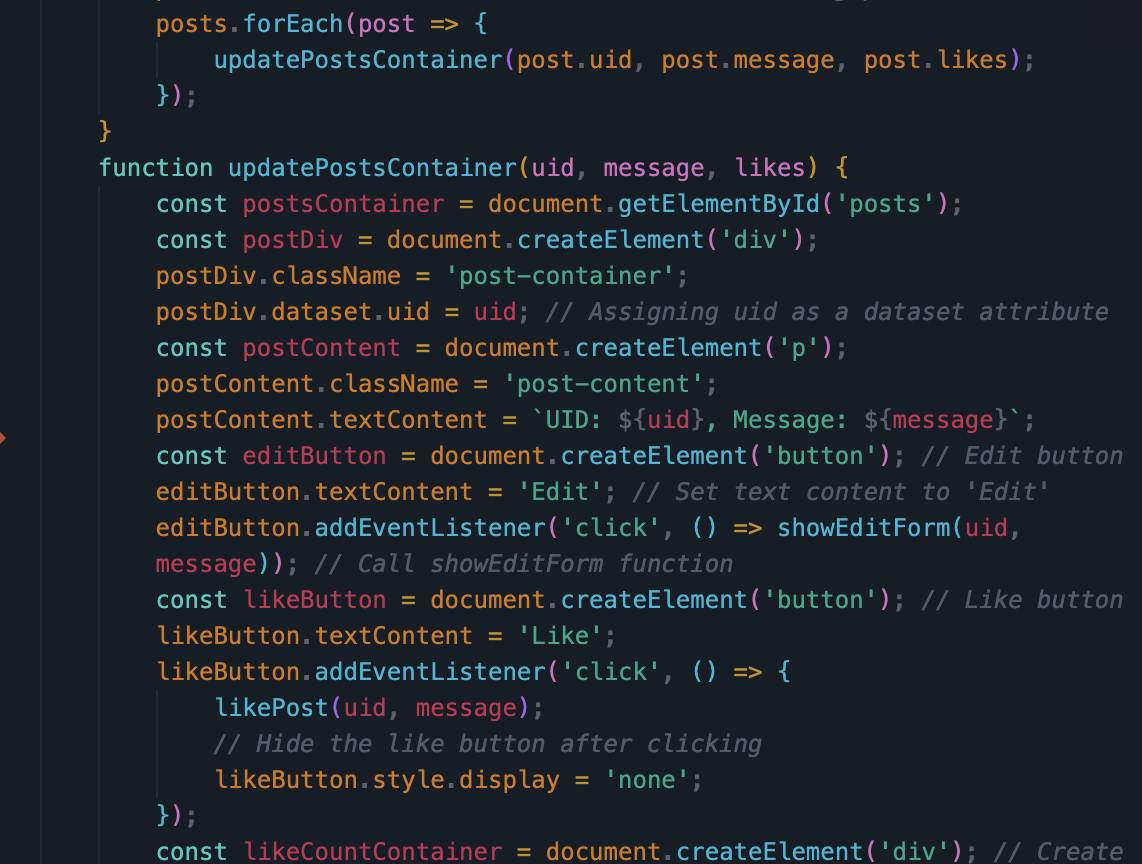
- For each post in posts, a new box is added. Each box displays the user’s name, message, and like counter
- In the Chrome browser, show a demo (POST or UPDATE) gathering and sending input and receiving a response that show update. Repeat this demo showing both success and failure.

- Via the text box, the users can send a POST request in the form of a new message to be added to the DB/displayed on the messages page
- In JavaScript code, show and describe code that handles success. Describe how code shows success to the user in the Chrome Browser screen.
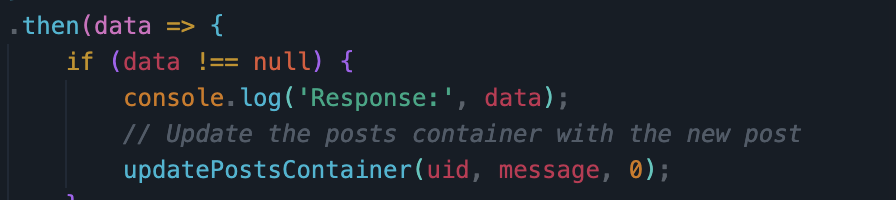
- Upon the success of the fetch function, the posts display container will be updated to show the new container
- In JavaScript code, show and describe code that handles failure. Describe how the code shows failure to the user in the Chrome Browser screen.
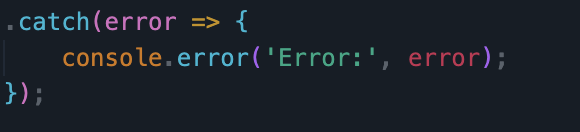
- If the data isn’t sent properly/an error occurs, the message is aborted and nothing new is shown to the user.
Machine Learning Algorith Analysis
- Show algorithms and preparation of data for analysis
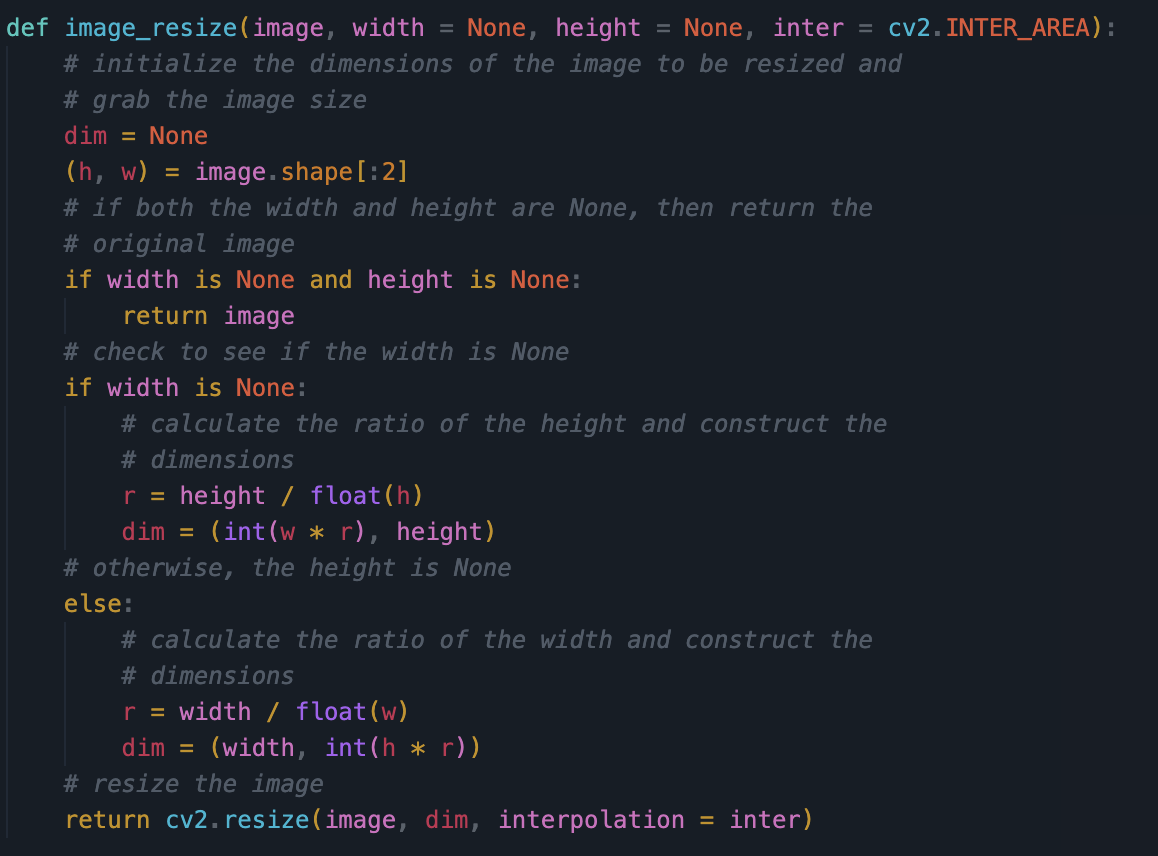
- Makes sure the pixel count of the image (width x height) matches what the model feeds into the input layer for proper analysis of data
- Show algorithms and preparation for predictions
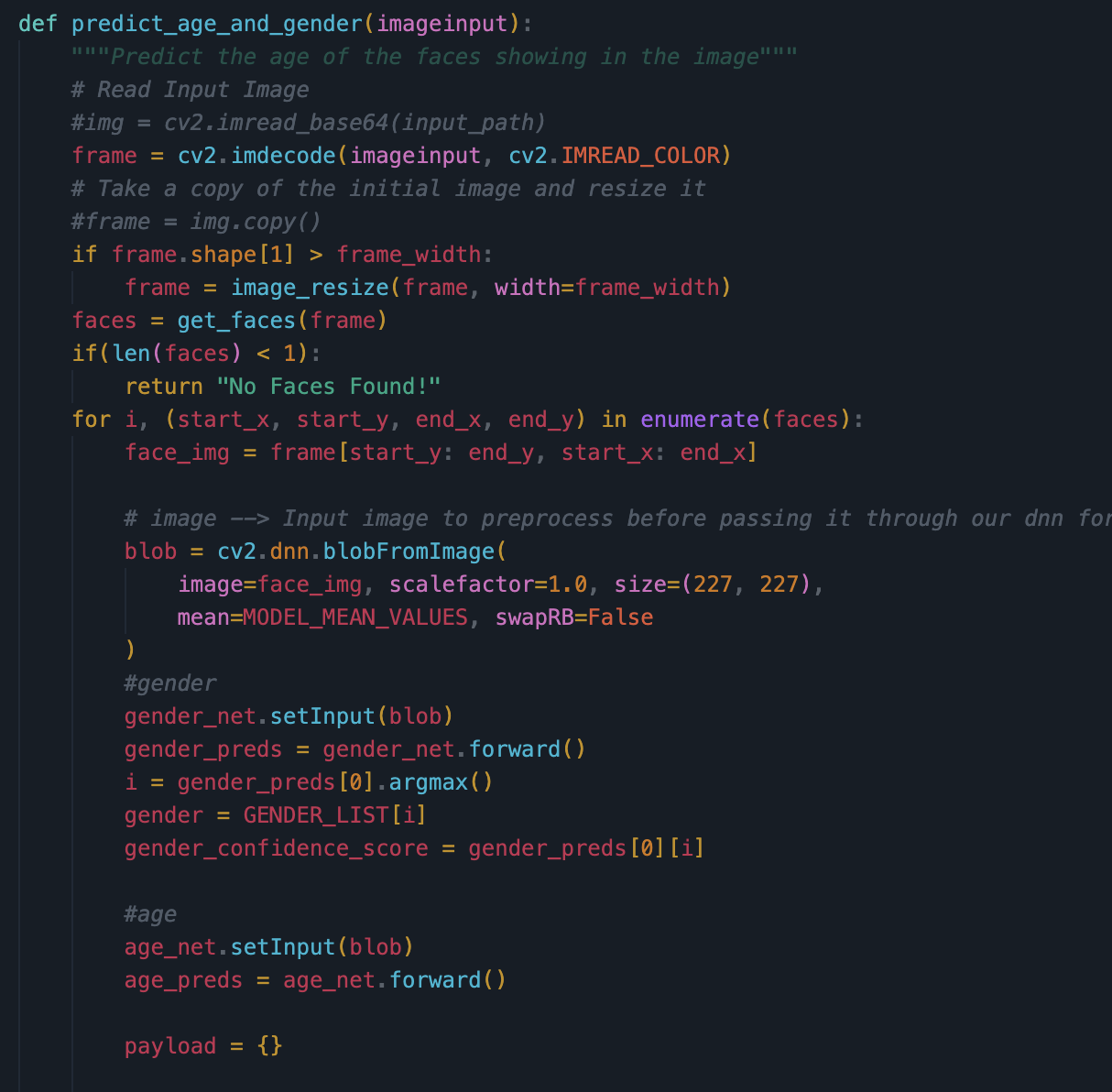
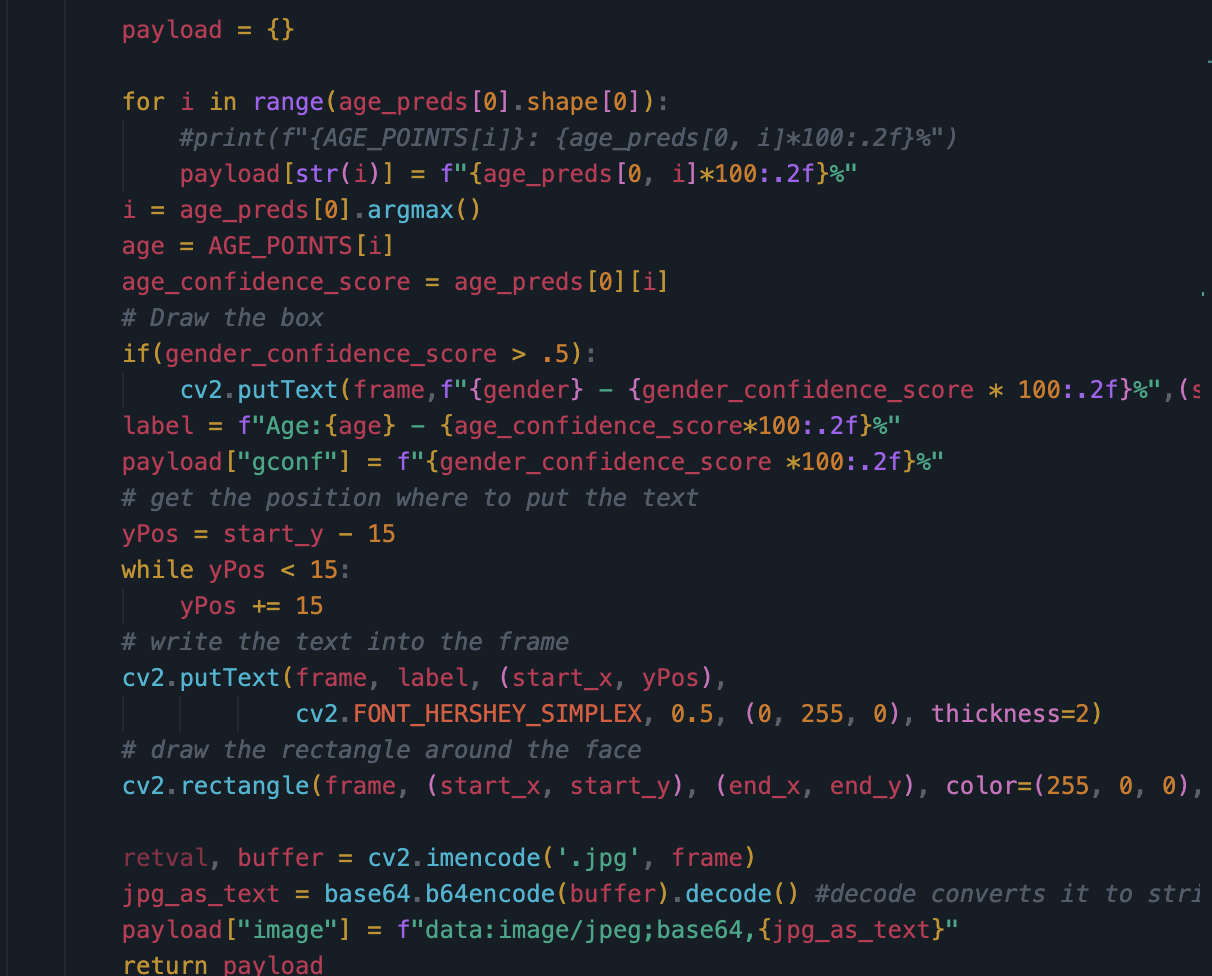
- Model detects the face in the image and gets the width and height of the face using OpenCV. The model does this by recognizing what pattern of pixels is similar to a human face by applying filters to the image data (image data is filtered into 3 channels for each color). Then the model resizes the data to fit the input layer of the age/gender detection model using the same process as the first step. The output is decoded from the output neuron then converted into a percent and sent to frontend for display.
- Linear Regression
- Linear Regression models create a line of best fit by minimizing the distance from each point in the given data without overfitting. This allows for an accurate prediction of some data based of inputted data.
- Decision Trees
- Decision Tree models use multiple features of data in a database to predict the value of another column (typically true/false output, can also be modified for multi-class classification). The inputted data is passed through nodes that split into other nodes, and at the end of the decision tree there are “terminal nodes” that give the output for the predicted value.


























